Java Loops
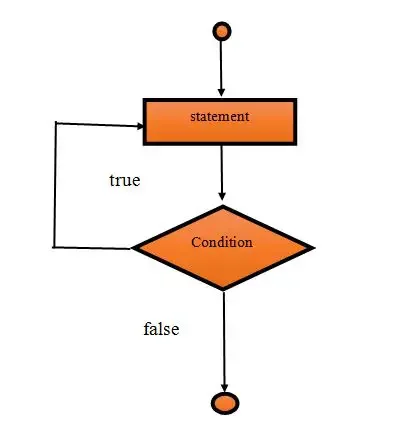
Table of Contents
Java Loops
Java Loops
The programming concept of a loop, which enables iteration over a series of statements, is crucial. The purpose of a loop is to execute a specific code block until the specified condition is met or until all elements of a collection (such as an array, list, or other collection) have been traversed. Loops are most frequently used to carry out repetitive tasks. For instance, we must write the print statement 10 times if we want to print a table of numbers. However, by using a loop, we can achieve the same result with a single print statement. The purpose of a loop is to keep running its block until the desired condition is met.
Java provides mainly three JAVA loops based on the loop structure.
We will explain each loop individually in details in the below.
For Loop
The for loop is used for executing a part of the program repeatedly. When the number of execution is fixed then it is suggested to use for loop. For loop can be categories into two type.
- for loop
- for-each loop
For Loop Syntax:
Following is the syntax for declaring for loop in Java.
for(initialization;condition;increment/decrement)
{
//statement
}
For loop Parameters:
To create a for loop, we need to set the following parameters.
1) Initialization
It is the initial part, where we set initial value for the loop. And It is executed only once at the starting of loop. It is optional, if we don’t want to set initial value.
2) Condition
It is used to test a condition each time while executing. The execution continues until the condition is false. It is optional and if we don’t specify, loop will be infinite.
3) Statement
It is loop body and executed every time until the condition is false.
4) Increment/Decrement
It is used for set increment or decrement value for the loop.
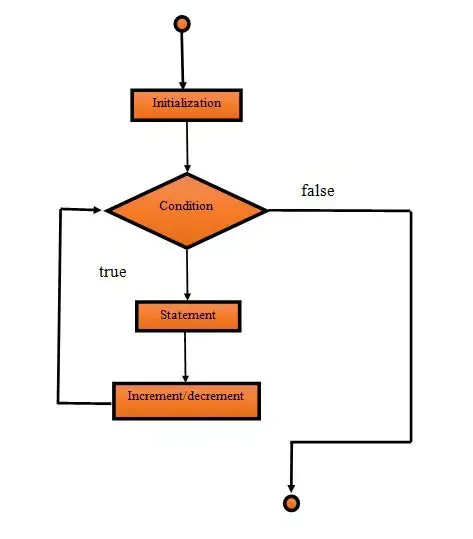
Data Flow Diagram of for loop
This flow diagram shows flow of the loop. Here we can understand flow of the loop.
For loop Example
In this example, initial value of loop is set to 1 and incrementing it by 1 till the condition is true and executes 10 times.
public class ForDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n, i;
n=2;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println(n+"*"+i+"="+n*i);
}
}
}
Example for Nested for loop
Loop can be nested, loop created inside another loop is called nested loop. Sometimes based on the requirement, we have to create nested loop.
Generally, nested loops are used to iterate tabular data.
public class ForDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(inti=1;i<=5;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
for-each Loop
In Java, for each loop is used for traversing array or collection elements. In this loop, there is no need for increment or decrement operator.
For-each loop syntax
Following is the syntax to declare for-each loop in the Java.
for(Type var:array)
{
//code for execution
}
Example:
In this example, we are traversing array elements using the for-each loop. For-each loop terminates automatically when no element is left in the array object.
public class ForEachDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
inta[]={20,21,22,23,24};
for(int i:a)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
While Loop
Like for loop, while loop is also used to execute code repeatedly. a control statement. It is used for iterating a part of the program several times. When the number of iteration is not fixed then while loop is used.
Syntax:
while(condition)
{
//code for execution
}
Data-flow-diagram of While Block
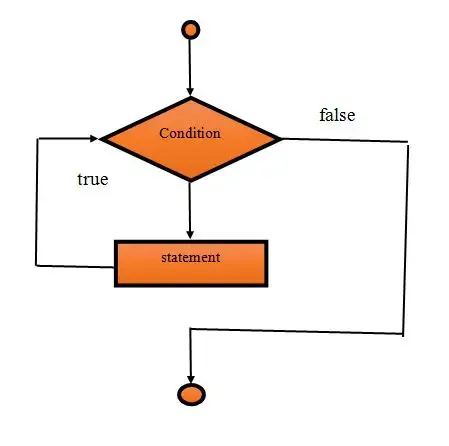
Example:
In this example, we are using while loop to print 1 to 10 values. In first step, we set conditional variable then test the condition and if condition is true execute the loop body and increment the variable by 1.
public class WhileDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
inti=1;
while(i<=10)
{
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
Example for infinite while loop
A while loop which conditional expression always returns true is called infinite while loop. We can also create infinite loop by passing true literal in the loop.
Be careful, when creating infinite loop because it can issue memory overflow problem.
public class WhileDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
while(true)
{
System.out.println("infinitive while loop");
}
}
}
do-while loop
In Java, the do-while loop is used to execute statements again and again. This loop executes at least once because the loop is executed before the condition is checked. It means loop condition evaluates after executing of loop body.
The main difference between while and do-while loop is, in do while loop condition evaluates after executing the loop.
Syntax:
Following is the syntax to declare do-while loop in Java.
do
{
//code for execution
}
while(condition);
Data Flow Diagram of do-while Block

Example:
In this example, we are printing values from 1 to 10 by using the do while loop.
public class DoWhileDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
inti=1;
do
{
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}
Example for infinite do-while loop
Like infinite while loop, we can create infinite do while loop as well. To create an infinite do while loop just pass the condition that always remains true.
public class DoWhileDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
do
{
System.out.println("infinitive do while loop");
}while(true);
}
}