Arrays and Pointers in C Programming
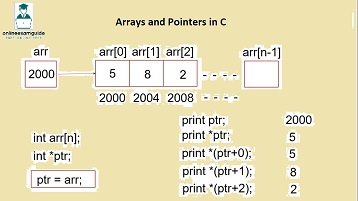
Table of Contents
C Programming Arrays and Pointers MCQ Questions and Answers on Basics to attend job placement exams, interview questions, college viva and Lab Tests
An Array is a group of elements of same data type. C Programming Language allows programmers to deal with maintainability of a C program with tens of hundreds of variables used for a specific purpose.
Arrays and Pointers
An Array can be thought of as Single Row of Chairs in a Cinema Theater. Each row has a Number. Also, each Chair in that row has a number.

Syntax of Array:
int pincodes[20]; //Array Declaration
Facts about Arrays:
- Every array has a Name which is nothing but the Variable Name.
- Every Array has a Size. It can NOT be be specified at run time or later.
- Every Array has a Data Type.
In the above array declaration, pincodes is an array variable with a capacity of 20 elements. All elements belong to int data type. Even before storing data in the array, memory is reserved in contiguous or continuous memory locations. These contiguous locations can be thought of as Reserved or Booked Chairs in a Cinema Theater.
Array Index Out of Bounds or accessing index more than array size does not produce any error. It simply shows garbage values. Java language shows errors or exceptions in this case.
Array size must be specified in between two Brackets [ ]. It is also called Subscript. A new word INDEX is used to identify the location or order of a particular element in an Array. Eg. pincodes [5] = 10;. Array index always starts with ZERO ‘0’. So pincodes[5] represents 6th element in the array.
Array elements can be used in all Arithmetic operations.
Array Initialization
By default, array elements are initialized with some default values even if you do not assign any value. Depending on the Storage Class, array elements get some default values. ‘auto’ and ‘register’ type array elements hold garbage values by default. ‘static’ and ‘extern’ type array elements hold ZERO as default values. By default, ‘auto’ storage class is applied.
//Declaration and Initialization
int pincodes[4] = {1234, 4321, 2345, 5432};
int marks[] = {98, 75, 89, 34, 28, 65};
int buses[3]; //Declaration
//Initialization
buses[0] = 23;
buses[1] = 56;
buses[2] = 34;
Array elements can be initialized at the time of Declaration it self. Usually, we assign values to array elements at run time or during execution of program like in buses example above.
Note that we have not specified array size for the variable marks. Because we are initializing the array at the same time. In the case of buses, specifying array size is mandatory as initialization is not done.
Arrays and Pointers mcq
Example 1
int main()
{
int marks[] = {23, 45, 78};
int num = 3, i=0;
for(i=num-1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("a[%d]=%d, ", i, marks[i]);
return 9;
}
//output
//a[2]=78, a[1]=45, a[0]=23,
In the above example, Array “marks” contains 3 elements. Array index starts from 0 and ends with 2.
C Programming Arrays and Pointers
Example 2: Passing array elements with / without Pointers
We can pass array elements to a function using Pass By Value and Pass By Reference. Pass By Reference is achieved using Pointers.
void display(int, int*);
int main()
{
int x=5, y=8;
display(x,y);
printf("%d, %d", x, y);
return 9;
}
//a = call by value
//*b = call by reference
void display(int a, int *b)
{
*b = *b + 1;
printf("%d, %d", a, b);
}
//OUTPUT
//5, 8
//5, 9
//8 becomes after incrementing using pointers
Multidimensional Arrays
An array with only one Subscript is called a Single Dimensional Array or 1D array. An array with more than one dimension is called a Multidimensional Array or nD array. A 2D array is composed of 1 row and 1 column. Size of an array is obtained by multiplying the sizes of individual 1D arrays. For example, students[2][3] represents the element present at 3rd row 4th column.
In a multidimensional array, specifying last subscript or Last Dimension is mandatory during combined declaration and initialization. If you are initializing elements later, mentioning all subscripts or dimension sizes are mandatory.
Example
int main()
{
//3 Rows each consisting of 2 columns.
//WE HAVE NOT MENTIONED ROW SIZE **********
int chairs[][2] = {{22,33},{44,55},{66,88}};
int i=0; j=0;
while(i<=(3-1))
{
while(j <= (2-1))
{
printf("%d,", chairs[i][j]);
j++;
}
printf("\n");
i++;
}
return 9;
}
//OUTPUT
//22,33,
//44,55,
//66,88
//Last element of this 2D array = chairs[2][1]
We have used WHILE loop instead of FOR loop in this example. Most of the developers use FOR loop to handle multidimensional arrays.
Using Pointers with Arrays
Arrays are handled internally using pointers. & Operator is called Address Of Operator. &a represents the address of variable ‘a’. * (STAR) operator is called VALUE AT ADDRESS operator. So *p represents the value at address if p is a pointer to an address.
To pass an array, we usually pass the Base Address or Address of First Element of an Array.
Arrays and Pointers examples
Example 1: Passing an array to a function
void show(int[]);
void show2(int *);
int main()
{
int a[3] = {3,4,5};
show(&a[0]); //We are passing base address
show2(&a[0]);
return 9;
}
void show(int k[])
{
printf("%d,", k[0]); //print 1st element
}
void show2(int *p)
{
p++; //points to 2nd element
printf("%d, *p);
}
//OUTPUT
//3,4,
Notes on Array Pointers
We use below code for notes.
int ary[3]; int *p = &ary[0]; int *q = ary; int cats[i]; int kites[i][j]; int bats[a][b][c];
1. ary[5] = *(p+4);
2. q[i] = i[q] = *(q+i) = *(i+q)
3. cats[ i ] = i [ cats] = *(cats+i) = *(i+cats)
4. kites[i][j] = *(*(kites+i) + j)
5. bats[a][b][c] = *(*(*(bats + a) + b) + c)
6. Incrementing an array pointer points to next memory location after skipping memory bytes of the data type
[WpProQuiz 34]
C Programming Arrays and Pointers MCQ
1) What is an Array in C language.?
A) A group of elements of same data type.
B) An array contains more than one element
C) Array elements are stored in memory in continuous or contiguous locations.
D) All the above.
Answer [=] D
2) Choose a correct statement about C language arrays.
A) An array address is the address of first element of array itself.
B) An array size must be declared if not initialized immediately.
C) Array size is the sum of sizes of all elements of the array.
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
3) What are the Types of Arrays.?
A) int, long, float, double
B) struct, enum
C) char
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
4) An array Index starts with.?
A) -1
B) 0
C) 1
D) 2
Answer [=] B
5) Choose a correct statement about C language arrays.
A) An array size can not changed once it is created.
B) Array element value can be changed any number of times
C) To access Nth element of an array students, use students[n-1] as the starting index is 0.
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
6) What is the output of C Program.? int main() { int a[]; a[4] = {1,2,3,4}; printf(“%d”, a[0]); }
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
If you do not initialize an array, you must mention ARRAY SIZE.
7) What is the output of C Program.? int main() { int a[] = {1,2,3,4}; int b[4] = {5,6,7,8}; printf(“%d,%d”, a[0], b[0]); }
A) 1,5
B) 2,6
C) 0 0
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
It is perfectly allowed to skip array size if you are initializing at the same time. a[0] is first element.
int a[] = {1,2,3,4};
8) What is the output of C Program.? int main() { char grade[] = {‘A’,’B’,’C’}; printf(“GRADE=%c, “, *grade); printf(“GRADE=%d”, grade); }
A) GRADE=some address of array, GRADE=A
B) GRADE=A, GRADE=some address of array
C) GRADE=A, GRADE=A
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
Variable grade = address of first element. *grade is the first element of array i.e grade[0].
9) What is the output of C program.? int main() { char grade[] = {‘A’,’B’,’C’}; printf(“GRADE=%d, “, *grade); printf(“GRADE=%d”, grade[0]); }
A) A A
B) 65 A
C) 65 65
D) None of the above
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
*grade == grade[0]. We are printing with %d not with %c. So, ASCII value is printed.
10) What is the output of C program.? int main() { float marks[3] = {90.5, 92.5, 96.5}; int a=0; while(a<3) { printf(“%.2f,”, marks[a]); a++; } }
A) 90.5 92.5 96.5
B) 90.50 92.50 96.50
C) 0.00 0.00 0.00
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
0.2%f prints only two decimal points. It is allowed to use float values with arrays.
11) What is the output of C Program.? int main() { int a[3] = {10,12,14}; a[1]=20; int i=0; while(i<3) { printf(“%d “, a[i]); i++; } }
A) 20 12 14
B) 10 20 14
C) 10 12 20
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
a[i] is (i+1) element. So a[1] changes the second element.
12) What is the output of C program.? int main() { int a[3] = {10,12,14}; int i=0; while(i<3) { printf(“%d “, i[a]); i++; } }
A) 14 12 10
B) 10 10 10
C) 10 12 14
D) None of the above
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
a[k] == k[a]. Use any notation to refer to array elements.
13) What is the output of C Program.? int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; a[0]++; int i=0; while(i<3) { printf(“%d “, i[a]); i++; } }
A) 20 30 40
B) 41 30 20
C) 21 30 40
D) None of the above
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
You can use increment and decrement operators on array variables too.
14) What is the output of C program with arrays.? int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; int b[3]; b=a; printf(“%d”, b[0]); }
A) 20
B) 30
C) address of 0th element.
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
You can assign one array variable to other.
15) What is the output of C Program with arrays and pointers.? int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; int (*p)[3]; p=&a; printf(“%d”, (*p)[0]); }
A) 20
B) 0
C) address of element 20
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
You can not directly assign one array variable to other. But using an array pointer, you can point to the another array. (*p) parantheses are very important.
16) What is the output of C program with arrays and pointers.? int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; int *p[3]; p=&a; printf(“%d”, *p[0]); }
A) 20
B) address of element 20
C) Garbage value
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
To point to an array, array pointer declaration should be like (*p)[3] with parantheses. It points to array of 3 elements.
17) What is the output of C program with arrays and pointers.? int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; printf(“%d”, *(a+1)); }
A) 20
B) 30
C) 40
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
*(a+0) == *a == a[0]. So *(a+1) is element at index 1. Index starts with ZERO.
18) What is an array Base Address in C language.?
A) Base address is the address of 0th index element.
B) An array b[] base address is &b[0]
C) An array b[] base address can be printed with printf(“%d”, b);
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
19) What is the output of C Program with arrays and pointers.? void change(int[]); int main() { int a[3] = {20,30,40}; change(a); printf(“%d %d”, *a, a[0]); } void change(int a[]) { a[0] = 10; }
A) 20 20
B) 10 20
C) 10 10
D) 20 30
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Notice that function change() is able to change the value of a[0] of main(). It uses Call By Reference. So changes in called function affected the original values.
20) An entire array is always passed by ___ to a called function.
A) Call by value
B) Call by reference
C) Address relocation
D) Address restructure
Answer [=] B
21) What is the output of C program with arrays and pointers.?
int main()
{
int size=4;
int a[size];
a[0]=5;a[1]=6;
a[2]=7;a[3]=8;
printf("%d %d", *(a+2), a[1]);
}
A) 8 6
B) 7 6
C) 6 6
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
variable size is already defined. So a[size] is allowed. *(a+2) == a[2].
22) What is the output of C program with arrays.?
int main()
{
int ary(3)=[20,30,40];
printf("%d", a(1));
}
A) 20
B) 30
C) 0
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
Array should be declared and defined with Square Brackets. Use ary[2] instead of ary(2).
int ary[3]={20,30,40};
23) What is the output of C Program with arrays.?
int main()
{
int rollno[3]=[1001,1002,1003];
printf("%d", rollno[1]);
}
A) 1002
B) 1003
C) address of 1002
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
You should use Flower Brackets or Braces to define elements like {1,2,3}. It is wrong to use [1,2,3].
24) What is the output of C program with arrays.?
int main()
{
char grade={'A','B','C'};
printf("%c", grade[0]);
}
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
Notice that char grade is an character variable, not Character array variable. So declare as char grade[] = {‘A’,’B’,’C’};
25) What is the value of an array element which is not initialized.?
A) By default Zero 0
B) 1
C) Depends on Storage Class
D) None of the above.
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
For Automatic variables, default value is garbage. For static and global variables, default value is 0.
26) What happens when you try to access an Array variable outside its Size.?
A) Compiler error is thrown
B) 0 value will be returned
C) 1 value will be returned
D) Some garbage value will be returned.
Answer [=] D
27) What is the size of an array in the below C program statement.?
int main()
{
int ary[9];
return 0;
}
A) 8
B) 9
C) 10
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
Size of array is 9. As a result, the CPU reserves 9 integers’ worth of memory.
28) What is the minimum and maximum Indexes of this below array.?
int main()
{
int ary[9];
return 0;
}
A) -1, 8
B) 0, 8
C) 1,9
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
Array index starts with 0 and ends with 8 for a 9 Size array. ary[0] to ary[8] are meaningful.
29) Can we change the starting index of an array from 0 to 1 in any way.?
A) Yes. Through pointers.
B) Yes. Through Call by Value.
C) Yes. Through Call by Reference.
D) None of the above.
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
No. You can not change the C Basic rules of Zero Starting Index of an Array.
30) What is the need for C arrays.?
A) You need not create so many separate variables and get confused while using.
B) Using a single Array variable, you can access all elements of the array easily.
C) Code maintainability is easy for programmers and maintainers.
D) All the above.
Answer [=] D
31) What is the output of C program with arrays.?
int main()
{
int ary[4], size=4;
printf("%d ", ary[size]);
return 0;
}
A) 0
B) 1
C) Random number
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Yes. Due to the array’s lack of initialization and the index’s out-of-range value, some random number will be printed. However, you do not encounter a compiler error. Your responsibility is to do it.
32) What is the output of C Program with arrays.?
int main()
{
int ary[4];
ary[4] = {1,2,3,4};
printf("%d ", ary[2]);
return 0;
}
A) 2
B) 3
C) 0
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
After defining the array’s type and size, you cannot initialise it in the following line or statement.
int ary[4]={1,2,3,4}; //works
33) What is the output of C Program with arrays.?
int main()
{
int ary[3]={1,2};
printf("%d %d",ary[2]);
return 0;
}
A) 0
B) 2
C) Garbage value
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Though you initialized only two elements in a 3 Size array, it is valid. Third element is a garbage value.
34) What is a multidimensional array in C Language.?
A) It is like a matrix or table with rows and columns
B) It is an array of arrays
C) To access 3rd tow 2nd element use ary[2][1] as the index starts from 0 row or column
D) All the above.
Answer [=] D
35) If an integer array pointer is incremented, how many bytes will be skipped to reach next element location.?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 8
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
In Turbo C, integer occupies 2 bytes. So in an integer array, if array pointer is incremented, it will reach the next element after two bytes. In this below 4 element integer array, elements are available at 1001, 1003, 1005 and 1007 byte addresses.
1001 1002 1003 1004 1005 1006 1007 1008.
36) What is the output of C Program with arrays and pointers.?
int main()
{
int ary[] = {10,20,30}, *p;
p = &ary[0];
int i=0;
while(i<3)
{
printf("%d ", *p);
p++;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
A) 10 10 10
B) 10 20 20
C) 10 20 30
D) randomvalue randomvalue randomvalue
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
First get the address of 1st element &ary[0]. Increment the pointer P to reach next element of the array.
37) What is the function used to allocate memory to an array at run time with Zero initial value to each.?
A) calloc()
B) malloc()
C) palloc()
D) kalloc()
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
Yes. calloc() initialized the elements to 0. malloc() does not initialize. So garbage values will be there.
38) What is the function used to allocate memory to an array at run time without initializing array elements.?
A) calloc()
B) malloc()
C) palloc()
D) kalloc()
Answer [=] B
39) Choose a correct Syntax for malloc() function to allocate memory to an array at run time.
A)
int *p; p = (int*)malloc(10*sizeof(int));
B)
int *p; p = (int*)malloc(10,sizeof(int));
C)
int *p; p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int), 10);
D)
int *p; p = (int*)malloc(10*sizeof(int *));
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
It allocates memory to hold 10 integers in an array.
40) What is the syntax of CALLOC to allocate memory to an array at runtime.?
A)
int *p; p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int));
B)
int *p; p = (int*)calloc(10*sizeof(int));
C)
int *p; p = (int*)calloc(sizeof(int), 10);
D)
int *p; p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int *));
Answer [=] A