Cavitation, abrasion, attrition, corrosion, and hydraulic action
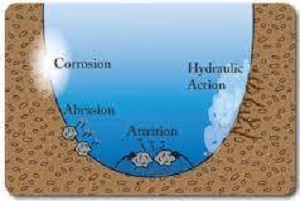
Table of Contents
Cavitation, abrasion, attrition, corrosion, and hydraulic action
Cavitation:
Running water performs a distinct and uncommon type of hydraulic action. It is most frequently seen in areas where river water suddenly picks up an unusually high velocity, like near a waterfall. To put it another way, at that point there is a spontaneous transition from a liquid to a vapour state and back to a liquid state. Hydropower generation projects have also been known to experience cavitations.
Hydraulic action:
The material is mechanically loosened and removed from the rocks as a result of the pressure from the flowing water. The ability of the flowing water to physically remove rock or soil grains from the parent body. That are present at the base or sides increases as the flow rate does. When a river is moving quickly enough, it frequently creates forces that are powerful enough to break up loose rocks, move the fragments that were created as a result, and lift and move the fragments as part of the bed load.
Abrasion:
It is the main method of stream erosion and entails wearing down the bedrock and rocks along a stream or river’s banks by the flowing water with the aid of sand grains, pebbles, gravels, and all other such particles that are being carried by its as load. These particles grains and rock fragments moving along with river water are collectively known as tolls of erosion. Some of the most well-known examples formed primarily by river abrasion include river terraces, gorges, canyons, escarpments, and river valleys.
Attrition:
This phrase (attrition) refers to the damage sustained by the load sediments during their transport by a moving natural agency as a result of collisions and mutual impacts. Every component of the sediment load that is suspended or moving along the stream bed is repeatedly impacted by other particles. The irregularities and angularities of the particles are worn out as a result of these mutual collusions. These develop a spherical outline, are rounded, and have polished surfaces. Some of the fragments eventually become very small particles that can be easily transported by running water over long distances.
Corrosion:
Corrosion is the term used to describe the gradual, steady chemical action of stream water on rocks. Both the composition of the flowing water and the composition of the rocks affect how much corrosion occurs. As a result, not all rocks are equally vulnerable to stream water’s corrosive effects. To varying degrees, gypsum, rock salt, and limestones are soluble in water. Sandstones, quartzites, granites, and gneisses may hardly be corroded by the steam.