Boolean Algebra
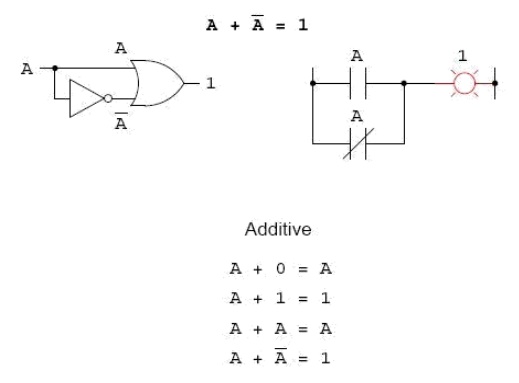
Table of Contents
Boolean Algebra – OR Gate , AND Gate , NAND GATE
Boolean Algebra
Let us begin our exploration of Boolean algebra by adding numbers together:
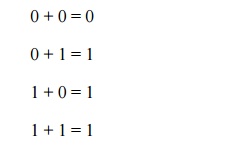
The first three sums make perfect sense to anyone familiar with elementary addition. The Last sum, though, is quite possibly responsible for more confusion . Than any other single statement in digital electronics, because it seems to run contrary to the basic principles of mathematics.
Well, it does contradict principles of addition for real numbers, but not for Boolean numbers. Remember that in the world of Boolean algebra . There are only two possible values for any quantity and for any arithmetic operation: 1 or 0. There is no such thing as ‖2‖ within the scope of Boolean values. Since the sum ‖1 + 1‖ certainly isn‘t 0, it must be 1 by process of elimination.
Boolean Algebra
OR Gate : ( Addition Logic)
Boolean addition corresponds to the logical function of an ‖OR‖ gate, as well as to parallel switch contacts:
There is no such thing as subtraction in the realm of Boolean mathematics. Subtraction Implies the existence of negative numbers: 5 – 3 is the same thing as 5 + (-3), and in Boolean algebra negative quantities are forbidden. There is no such thing as division in Boolean mathematics, either, since division is really nothing more than compounded subtraction, in the same way that multiplication is compounded addition.
Boolean Algebra
AND Gate : ( Multiplication – logic)
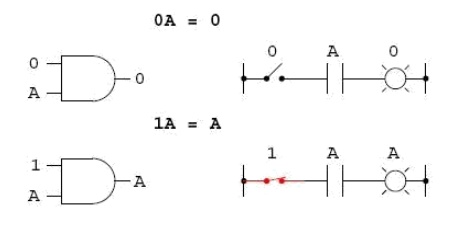
Multiplication is valid in Boolean algebra, and thankfully it is the same as in real-number algebra: anything multiplied by 0 is 0, and anything multiplied by 1 remains unchanged:
0 × 0 = 0
0 × 1 = 0
1 × 0 = 0
1 × 1 = 1
ty is that the sum f anything nd zero is the same as the ‖anything.‖ This identity is no sumand 0,is so equal we cannot to the original say that quantity: A+A= 02A+.0 Thus,=0, and when 1 +we 1 original=add1. Boolean quantity to itself, the (x + x = 2x), but remember th there is no concept of ‖2‖ the w rld of Boolean math, only 1 Introducing the uniquely Boolean concept of complementation into an additive identity, we find an interesting effect. Since there must be one ‖1‖ value between any variable and its complement, and since the sum of any Boolean quantity and 1 is 1, the sum of a variable and its complement must be 1:

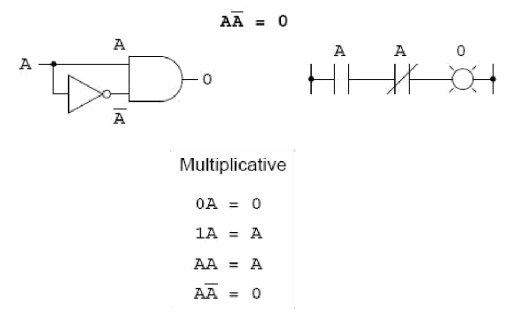
Four multiplicative identities: Ax0, Ax1, AxA, and AxA‘. Of these, the first two are no different from their equivalent expressions in regular algebra:
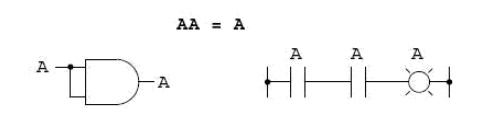
The third multiplicative identity expresses the result of a Boolean quantity multiplied by itself. In normal algebra, the product of a variable and itself is the square of that variable (3x 3 = 32 = 9). However, the concept of ‖square‖ implies a quantity of 2, which has no meaning in Boolean algebra, so we cannot say that A x A = A2. Instead, we find that the product of a Boolean quantity and itself is the original quantity, since 0 x 0 = 0 and
1 x 1 = 1:
The fourth multiplicative identity has no equivalent in regular algebra . Because it uses the complement of a variable, a concept unique to Boolean mathematics. Since there must be one ‖0‖ value between any variable and its complement, and since the product of any Boolean quantity and 0 is 0, the product of a variable and its complement must be 0:
Principle of Duality:
It states that every algebraic expression is deducible from the postulates of Boolean algebra . And it remains valid if the operators & identity elements are interchanged. If the inputs of a NOR gate are inverted we get a AND equivalent circuit. Similarly when the inputs of a NAND gate are inverted, we get a OR equivalent circuit. This property is called DUALITY.