Arithmetic Operators in Java Tutorial and MCQ
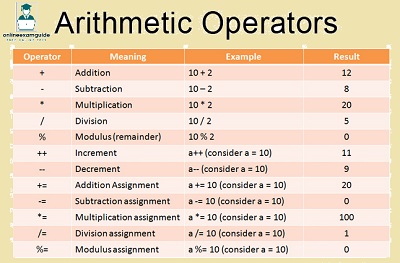
Table of Contents
Study and learn Java Programming Arithmetic Operators questions and answers on Arithmetic Operators and their priorities. Attend job interviews easily with these Multiple Choice Questions
Java Arithmetic Operators in Java
Java programming language provides Arithmetic operators like Addition (+), Subtraction (-), Multiplication (*), Division (/), Modulo Division (%), Increment (++) and Decrement (–) Operators with examples. You will also learn about Compound Assignment Operators. Arithmetic operators are comparable to Mathematical Algebraic Arithmetic operators. In the end, you will also learn Arithmetic Operator Priority or Precedence.
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are a must to create a java project of any size. You will learn about arithmetic operators with examples here in this tutorial.
| NO | Arithmetic Operators | Simple Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Addition Operator + | Plus |
| 2 | Subtraction Operator – | Minus |
| 3 | Multiplication Operator * | Into |
| 4 | Division Operator / | Divided By |
| 5 | Modulo Division Operator % | Remainder |
| NO | Arithmetic Operators | Simple Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Increment Operator ++ | Plus Plus |
| 2 | Decrement Operator — | Minus Minus |
| 3 | Unary Plus + | Plus Before |
| 4 | Unary Minus – | Minus Before |
Addition Operator +
Addition operator or Plus operator requires two operands left and right. It does the sum of two operands, variables or constants.
Subtraction Operator –
Subtraction operator or Minus operator requires two operands left and right. It does the subtraction of the second operand from the first operand.
Multiplication Operator *
Multiplication operator or Star operator or Into operator multiplies the first operand with the second operand. The data type of the result is dependent on the highest data type of one of the operands. However, you can use explicitly type casting to convert the result to the desired data type. The same rule applies to other arithmetic operators too.
Division Operator /
Division operator or Divided By operator divides the first operand with the second operand. The data type of the result is dependent on the highest data type of one of the operands. If all operands are integers, there will be precision loss after a division operation.
Modulo Division Operator %
Java provides a Remainder operator which is also called a Modulo Division Operator. Its symbol is a “Percentage”. Modulus operator works with both integers and floating point numbers.
Increment Operator ++
Java increment operator ++ works with just one operand. A prefixed increment operator increments the value of a variable by 1. Prefixed incrementing is done even before addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or modulo division. A postfixed increment operator increments the value of a variable after its old value is used in the arithmetic expression. The new value is available for the next or subsequent expressions.
Decrement Operator —
Java decrement operator — works with just one operand. A prefixed Decrement operator decrements the value of a variable by 1. Prefixed decrementing is done even before addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or modulo division. A postfixed Decrement operator decrements the value of a variable after its old value is used in the arithmetic expression. The new value is available for the next or subsequent expressions on the next line of code.
Unary Plus Operator +(operand)
Java unary plus operator + works with just one operand.
Unary Minus Operator -(operand)
Java unary minus operator + works with just one operand. Unary Minus ( – ) is applied to an operand even before addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or modulo division.
Code Example 1: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication
class Arithmetic1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5, b=10;
float c=4.5f, d=10.5f;
float e = a + c + b*d - 1;
System.out.println("OUTPUT= " + e);
int k = 1 - - 2; // 1 + 2
//Minus * Minus = PLUS
System.out.println("K=" + k);
}
}
//5 + 4.5 + (10*10.5) -1
//5 + 4.5 + 105 -1
//5 + 4.5 + 104
//5 + 108.5
//OUTPUT= 113.5
//k=1+2=3
Code Example 2: Division, Modulo Division
class Arithmetic2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5, b=12;
float c = b/a; //2.0
float d = (1.0f * b)/a; //2.4
float e = b%a; //2.0
float f = 56.5f%40; //16.5
}
}
//5 + 4.5 + (10*10.5) -1
//5 + 4.5 + 105 -1
//5 + 4.5 + 104
//5 + 108.5
//OUTPUT= 113.5
Code Example 3: Prefix Increment Operator, Prefix Decrement Operator
Prefix Increment or Prefix Decrement operators are evaluated first and then the expression is evaluated.
class Arithmetic3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5, b=12;
++a; //6
int c = --a + (++b); //5 + 13
System.out.println(c);
}
}
//OUTPUT= 18
Code Example 4: Postfix Increment Operator, Postfix Decrement Operator
Postfix Increment and Postfix Decrement operators are given less importance. So the old value is used to evaluate arithmetic expressions and then the increment or decrement operation is carried out.
class Arithmetic4
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5, b=12;
a++; //6
int c = (a--) + (b++); //6 + 12
System.out.println("C= " + c); //18
System.out.println("A=" +a + ", B=" + b ); //5, 13
int d = (b++) + (--a); //13 + 4
System.out.println("D= " + d); //17
System.out.println("A=" +a + ", B=" + b ); //A=4, B=14
}
}
//C= 18
//A=5, B=13
//D= 17
//A=4, B=14
Compound Assignment Operators / Shorthand Assignment Operators in Java
Compound Assignment operators in Java are a combination of Equal To ‘=’ and Arithmetic operators like Addition (Plus), Subtraction (Minus), Multiplication (Into), Division (Divided By) and Modulo Division (Remainder). These operators are part of Java arithmetic operators. These operators do not bring any performance improvements. It is only a convenience for developers to type less and let the compiler expand the compound assignment operators to full expressions before compiling.
| NO | Operator | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | += | a+=b a = a +b |
| 2 | -= | a -= b a = a-b |
| 3 | *= | a *= b a = a*b |
| 4 | /= | a /= b a = a |
| 5 | %= | a %= b a = a%b |
Syntax:
variable operator= expression (or) variable = variable + expression "operator=" is called Compound Assignment Operator.
Code Example 1: Compound Assignment Operator or Shorthand Assignment Operator
Shorthand assignment operators or Compound assignment operators are handy to use and easy to understand.
class Arithmetic5
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5, b=12;
a += 6; //a=a+6 = 5+6 = 11
b *= 4; //b=b*4 = 12*4 = 48
int c = b;
c %= 10; //c=c%10 = 48%10 = 8
int d = a;
a /= 2; //a=a/2 = 11/2 = 5;
}
}
Arithmetic Operators Priority or Precedence
Each arithmetic operators in Java is given a certain priority compared to other operators. Priority is also called Precedence. Knowledge of Operator Priority or Precedence is mandatory to construct and evaluate proper arithmetic expressions.
| Priority | Operator |
|---|---|
| 1 | Increment ++, Decrement –, Unary Minus – |
| 2 | Multiplication *, Division /, Modulo Division % |
| 3 | Addition +, Subtraction – |
| 4 | Assignment = |
Notice that Plus and Minus have got less priority than Multiplication, Division and Modulo Division operators. So addition or subtraction is performed last from left to right order in an arithmetic mathematical expression. All assignments (=) are carried out only after completion of all other arithmetic operations.
Note 1: Presence of Parentheses change the priority of evaluation. You can specify clearly which operands or expressions to be evaluated first. Using parentheses is a good programming practice as it helps other developers to understand our code easily.
Note 2: If there is a TIE between operators because of equality, simply follow Left to Right Evaluation.
Arithmetic Operators Precedence or Priority Example
class Arithmetic6
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=10, b=2, c=4, d=9;
float res = a + b * 4 / c % 3 + d;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
//Output: 21.0
//10 + 2 * 4 / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (2 * 4) / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (8) / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (8/4) % 3 + 9
//10 + (2) % 3 + 9
//10 + (2 % 3) + 9
//10 + 2 + 9 //LEFT TO RIGHT EVALUATION
//(10+2) + 9
//12 + 9
//21
Arithmetic Operators Precedence or Priority Example 2
Here in this example, increment operator before ‘b’ dominates other operators. Also, it is a prefix increment operator.
class Arithmetic7
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=10, b=2, c=4, d=9;
float res = a + ++b * 4 / c % 3 + d;
System.out.println(res);
}
}
//Output: 19.0
//10 + (++b) * 4 / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (3) * 4 / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (3 * 4) / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (12) / 4 % 3 + 9
//10 + (12/4) % 3 + 9
//10 + (3) % 3 + 9
//10 + (3 % 3) + 9
//10 + 0 + 9
//10 + 9
//19
In the next chapters or tutorials, we shall explore other types of Operators present in Java Language.
[WpProQuiz 66]
Arithmetic Operators in Java MCQ
1) An Arithmetic expression in Java involves which Operators or Operations?
A) Addition (+), Subtraction (-)
B) Multiplication (*), Division (/)
C) Modulo Division (%), Increment/Decrement (++/–), Unary Minus (-), Unary Plus (+)
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
2) Choose the Compound Assignment Arithmetic Operators in Java below.
A) +=, -=
B) *=, /=
C) %=
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
3)
What is the output of the below Java code snippet? int a = 2 - - 7; System.out.println(a);
A) -5
B) 10
C) 9
D) Compiler Error
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Minus of Minus is Plus. So 2 - - 7 becomes 2+7.
4)
What is the output of Java code snippet below? short p = 1; short k = p + 2; System.out.println(k);
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
Numbers are treated as int type by default. So an int value cannot be assigned to a short variable. You have to type cast the whole expression.
short k = (short)(p + 2);
5)
What is the output of Java code snippet? short k=1; k += 2; System.out.println(k);
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Compiler error about Type Casting
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Compound assignment operators automatically convert the expression value to the left-hand side data type.
k = k + 1; //Error k += 1; //Works k++; //Works
6)
What is the output of the Java code snippet? int a=5, b=10, c=15; a -= 3; b *= 2; c /= 5; System.out.println(a +" " + b + " " + c);
A) 2 20 3
B) 2 20 5
C) 2 10 5
D) -2 20 3
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
a = a - 3; b = b*2; c = c/5;
7)
How do you rewrite the below Java code snippet? int p=10; p = p%3;
A)
p=%3;
B)
p%=3;
C)
p=3%;
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
8) Which is the arithmetic operator in Java that gives the Remainder of Division?
A) /
B) @
C) %
D) &
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
//Modulo Division operator // or simply Modulus Operator int a = 14%5; //a holds 4 5)14(2 -10 ------ 4
9) Arithmetic operators +, -, /, * and % have which Associativity?
A) Right to Left
B) Left to Right
C) Right to Right
D) Left to Left
Answer [=] B
10) Between Postfix and Prefix arithmetic operators in Java, which operators have more priority?
A) Postfix operators have more priority than Prefix operators
B) Prefix operators have more priority than Postfix operators
C) Both Prefix and Postfix operators have equal priority
D) None of the above
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
op++, op– have more priority than –op, ++op.
11) Among Postfix Decrement and Prefix Increment operators in Java, which operator has less priority?
A) Postfix Decrement has less priority than Prefix Increment
B) Prefix Increment has less priority than Postfix Decrement
C) Both operators have same priority
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
a++ > ++b
12) Increment and Decrement arithmetic operators in Java has which Associativity?
A) Left to Right
B) Right to Left
C) Left to Left
D) Right to Right
Answer [=] B
13) Choose the correct statement about Java Operators +, -, *, / and %.
A) + and – have equal priority
B) * and / have equal priority
C) / and % have equal priority
D) All the above
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
All are having equal priority.
14) Among the operator groups (++, –) and (+, -, *, /, %) in Java, which group has higher priority?
A) (++, –) group has higher priority than (+, -, *, /, %) group
B) (++, –) group has lower priority than (+, -, *, /, %) group
C) (++, –) group and (+, -, *, /, %) group have equal priority
D) None of the above
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
Again between Prefix and Post operators, Postfix operators have higher priority.
15)
What is the output of the Java code snippet? int a=10, b=6; int c = a+b*5; System.out.println(c);
A) 40
B) 50
C) 80
D) Compiler error
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
* has higher priority than +. So, Multiplication operation is performed first.
a+(b*5) 10 + (6*5) 10 + 30 40
16)
What is the output of the Java code snippet? int a=10, b=5, c=3; int d = a+c/2*b; System.out.println(d);
A) 17.5
B) 32.5
C) 15
D) 30
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
/ and * have equal priority. So associativity of Left to Right is used. Remember that 3/2 is 1 not 1.5 as both operands are integers.
a+c/2*b a+(c/2*b) a + ( (c/2) * b) a + ( 3/2 * b) a + ( 1 * 5) 10 + 5 15
17)
What is the output of the Java code snippet?
int a=5, b=6;
if(a++ == --b)
{
System.out.println("5=5");
}
else
{
System.out.println("NONE");
}
A) NONE
B) 5=5
C) Compiler error
D) None of the above
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
At time of evaluating a++ == –b, a(5)is compared with –b(6-1). So, “if” condition passes. If you check a value after the ELSE block, it will be a+1 i.e 6.
18)
What is the output of the Java code snippet?
int a=6, b=5;
if(++b == a--)
{
System.out.println("RABBIT");
}
else
{
System.out.println("BUNNY");
}
A) RABBIT
B) BUNNY
C) Compiler error
D) None of the above
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
After the ELSE block, b will be b+1 i.e 6
++b == a-- ++b == (a-1) b == (a-1) 5 ==5
19)
What is the output of the Java code snippet? int a=10, b=20; int c = a++*2; int d = --b*2; System.out.println(c +"," + d);
A) 20,40
B) 22,40
C) 20,38
D) 22,38
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
The prefix is incremented or decremented immediately. Postfix incremented or decremented on the next line/statement.
1) a++*2 a*2 2) --b*2 (b-1)*2
20) Choose the correct statement about Java Prefix and Postfix operations.
A) Prefix operation is carried out immediately and the variable value will be incremented or decremented accordingly
B) Postfix operation is carried out on the next line or statement. So the variable value will not change.
C) A and B
D) None of the above
Answer [=] C