C Programming Arithmetic Operator
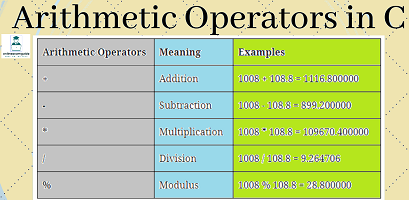
Table of Contents
Learn C Programming Arithmetic Operator MCQ Questions and Answers on Basics to attend job placement exams, interview questions, college viva and Lab Tests
C language comes with Arithmetic Operators like Plus, Minus, Multiplication, Division and Modulo Division. One more operator ‘=’, also called Assignment operator is also present.
C Programming Arithmetic Operators are used to work with integers and real numbers.
Study C basics and keywords before this tutorial.
Arithmetic Operator
| SNO | Operator | Description |
| 1 | + | Addition Operator |
| 2 | – | Subtraction Operator |
| 3 | * | Multiplication Operator |
| 4 | / | Multiplication Operator |
| 5 | % | Modulo Division Operator |
C Programming Arithmetic Operator
Example 1:
int main()
{
int a=5, b=10;
int c;
// = is Assignment operator
c = a + b;
printf("%d ", c);
c = a - b;
printf("%d ", c);
c = a*b;
printf("%d ", c);
c = b/a;
printf("%d ",c);
c = a%b; //modulo division or remainder operator
printf("%d", c);
return 0;
}
//output: 15 -5 50 2 5
Assignment Operator allows only right side value to be assigned to the left side variable. In the above program, left side variable ‘C’ gets the value of right side operation like addition, subtraction etc.
Note: Modulo division operator works only with whole numbers like integers.
Note: Arithmetic operators can also be applied on char variables as characters are converted to their respective ASCII codes before arithmetic operation.
Integer and Float Conversions
When you are working with integers and float (Real) numbers, some number conversions are applied.
- Result of int and int is integer only. Use %d format specifier. Use an int variable to hold data.
- Result of float and float is float only. Use %f format specifier. Use a float variable to hold data.
- Result of int and float is float only. Use %f format specifier. Use a float variable to hold data.
- If you use %d instead of %f, precision data will be lost.
- If you are working with long, double and long double data types, result of an arithmetic operation contains higher data type value. For example, arithmetic operation with short and int is always int.
Arithmetic Operator Example 1:
int main()
{
int a=5, b=10;
float c = 12.5f, d = 10.5f;
//int + int
printf("%d, ", a+b);
//float + float
printf("%f, ", c+d);
//int + float
printf("%f, ", a + c);
//int + float
printf("%d", a + c);
//%d truncates extra data i.e precision
return 0;
}
//output: 15, 23, 17.500000, 17
Example 2:
| SNO | Arithmetic Operation | Result |
| 1. | 9/2 | 4 |
| 2. | 9/2.0 | 4.5 |
| 3. | 9.0/2 | 4.5 |
| 4. | 9.0/2.0 | 4.5 |
| 5. | 2/9 | 0 |
| 6. | 2/9.0 | 0.22 |
| 7. | 2.0/9 | 0.22 |
| 8. | 2.0/9.0 | 0.22 |
Note: To avoid losing of precision data with division operator, multiply the numerator or denominator with 1.0f or 1.0 double value. Use parantheses ( ) operator to group all numerator or denominator expressions.
int main()
{
int a=10, b=4;
float c = (1.0f * a) / b;
//multiply with 1.0f or 1.0
printf("%f", c);
return 0;
}
//output: 2.500000
C Operator Precedence or Priority or Hierarchy
Each operator in C has a precedence or priority or hierarchy. Operator precedence is useful to evaluate arithmetic expressions with operators of different priority. Operator priority decides which operator and operands should be evaluated first.
Note: Constants on the left and right side of operator are called Operands.
Example 1:
int main()
{
int a=2, b=3, c=8;
int d=0;
d = a + b * c;
printf("%d", d);
return 9;
}
//output:
// 2 + (3*8)
// 2 + 24
// 26 is the output
//'*' operator has higher priority
// wrong = (a+b)*c
Arithmetic Operator Precedence Chart
| Priority | Operator | Description |
| 1st | *, /, % | Multiplication, Division, Modulo Division |
| 2nd | +, – | Addition, Subtraction |
| 3rd | = | Assignment |
Example 2:
int main()
{
float abc = 5 + 10 / 2 * 5 - 2 % 5;
printf("Result=%f", abc);
return 0;
}
//Evaluation steps
//10 / 2 * 5 left to right processing
//5 + 25 - 2 left to right processing
// START
// 5 + (10 / 2) * 5 - 2 % 5
// 5 + 5 * 5 - 2 % 5
// 5 + 25 - 2 % 5
// 5 + 25 - 2
// 30 - 2
// 28
//END
C Operator Associativity
C operator associativity deals with the problem of associating an operand to either left operator or right operator. When two equal priority operators are encountered in an expression, this Operator associativity is used to solve deadlock. Usually arithmetic operators follow Left to Right Associativity. Equals to ‘=’ operator follows Right to Left Associativity.
Example 1:
int d = 3 + 4 + 5;
Now as per Left to Associativity of arithmetic operators, 4 belongs to the left side + or first + operator. So the expression becomes (3+4) + 5. Next, the result of expression is added to 5 like (7)+5.
Now as per Right to Left Associativity of Equals to Operator, right side value is assigned to left side variable. So the variable d now holds a value of 12.
Example 2:
float fd = 3 + 12 / 5;
In the code above, there are two operators + and /. As Division / operator has higher priority, operand 12 is associated with /. instead of + on the left side. So 12/5 evaluates to 2. fd = 3 + 2 = 5 now.
learn C Programming Syntax Basics in this multipart tutorial which are useful for students in the last minute before exam. C Programming Language was invented by Dennis Ritchie in Bell Laboratories. Now Nokia owns Bell Laboratories and experiments are still going on.
C Programming Syntax Basics Part 1
We shall learn about basic structure of a C Program and predefined Keywords in this C Programming Syntax Basics Tutorial Part 1. You can set up a Turbo C Compiler on your Windows Machine easily.
Structure of a C Program
Every C program contains a function or method called main(). All functions end with Round Brackets or Paranthesis ( ). Inside Paratheses, arguments can be received or passed. Code of a Function is surrounded by Curly Brackets or Braces { }.
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
/*This is a multi-line comment.
It is not compiled or checked for Syntax*/
printf("Hello C..");
}
Output
Hello C..
Observations
- VOID is a return type. VOID means nothing is being returned.
- main() { } is a compulsory function in any C Program.
- void and main should be typed in lowercase completely.
- / symbol is called Forward Slash or simply Slash.
- * symbol is called STAR.
- /* */ is a multiline comment. Comments are useful for analysing code logic flow in very big projects. Comments make others easily understand your program or project.
- printf() is a function which is passing one argument “Helllo C”.
- “Hello C” is a string literal here.
- Code statements or lines end with Semicolon ;
- Putting a return type before a function name is not mandatory in a C Compiler. If you use a C++ Compiler to compile c programs, you must specify a return type.
- #include includes an already written header file stdio.h which contains code for printf function. Without predefined functions, life becomes difficult to write everything every time on our own. Also the code without including files becomes clumsy to maintain and understand.
Keywords in C Language
There are a total of 32 keywords in C Language which can not be used for the names of variables and functions. Find the C Programming Keyword list below. Students need to remember these keywords just like that to attempt questions asked in their exams.
| Keyword | Meaning |
| auto | Defines local life time for a variable |
| break | Breaks a current loop in general |
| case | Defines branch control point |
| char | Basic data type, character literal |
| const | Defines a Constant, unmodified variable |
| continue | control goes to the loop beginning |
| default | control point used in switch construct in general |
| do | do while loop |
| double | Floating point data type bigger than float type |
| else | Usually followed by if construct. If conditon fails, branch to else block |
| enum | Used to define a group of int constants like array |
| extern | Used to define a variable or function with type and the definition may exist some where |
| float | Floating point data type |
| for | For Loop |
| goto | Transfers execution control to defined Label |
| if | A conditional statement |
| int | Basic integer data type |
| long | Integer data type bigger than int |
| register | Tells to store the variable in RAM register |
| return | ends execution immediately |
| short | Type Modifier |
| signed | Type Modifier |
| sizeof | used to get the size of a variable. Eg. sizeof(integerType) |
| static | used to create a variable with broad scope |
| struct | Used to define a custom data type kind of thing |
| switch | switch branch control |
| typedef | used to create new type |
| union | used in grouping of variables of same type |
| unsigned | Modifiere used to increase positive max value |
| void | empty data type or return type |
| volatile | Used to create a variable with a value changed by any external process |
| while | while loop with a condition |
[WpProQuiz 25]
Arithmetic Operator interview MCQ
1) What is the Priority among (*, /, %), (+, -) and (=) C Operators.?
A) (*, /, %) > (+, -) < (=)
B) (*, /, %) < (+, -) < (=)
C) (*, /, %) > (+, -) > (=)
D) (*, /, %) < (+, -) (+, -) == (=)
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Assignment operator in C has the least priority.
2) What is the output of the C statement.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 4 + 4/2*5 + 20;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 40
B) 4
C) 34
D) 54
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
/ and * has equal priority. But associativity is from L to R.
4 + 2*5 + 20
4 + 10 + 20 = 34
3) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 10 + 5 * 2 * 8 / 2 + 4;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 124
B) 54
C) 23
D) 404
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
10 + 10*8/2 + 4
And 10 + 80/2 + 4
10 + 40 + 4 = 54
4) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 4 + 5/2*10 + 5;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 29
B) 5
C) 4
D) 34
Answer [=] A
Explanation:
5/2 is 2 only because both numerator and denominator are integers. So only int value i.e 2 is the result.
4 + 2 * 10 + 5
4 + 20 + 5 = 29.
5) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 10 + 2 * 12 /(3*2) + 5;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 31
B) 19
C) 11
D) 29
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
Paranthesis changes the associativity of operators.
10 + 2 * 12 / (3*2) + 5;
And 10 + 24 / (3*2) + 5;
10+ 24/6 + 5;
10 + 4 + 5 = 19;
6) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 10 + 2 * 12 / 3 * 2 + 5;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 19
B) 31
C) 11
D) 25
Answer [=] B
Explanation:
10 + 2 * 12 / 3 * 2 + 5;
And 10 + 24/3*2 + 5;
10 + 8*2 + 5;
10 + 16 + 5 = 31;
7) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
float a=10.0;
a = a % 3;
printf("%f", a);
return 0;
}
A) 0
B) 1
C) 1.000000
D) Compiler error.
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
You can use the operator Modulus Division % with only integers.
error: invalid operands to binary % (have ‘float’ and ‘int’)
a = a % 3;
^
8) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
float a=10.0;
a = (int)a % 3;
printf("%f", a);
return 0;
}
A) 0
B) 1
C) 1.000000
D) Compiler Error.
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Type casting from float to int is done by (int).
(int)10.000000 = 10;
10%3 = 1. Reminder of the division of 10 by 3.
%f in printf prints it as 1.000000.
9) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a=0;
a = 14%-5 - 2;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 0
B) -4
C) -2
D) 2
Answer [=] D
Explanation:
14%5 = 4 ( Reminder)
14 % -5 = 4. Yes sign of the reminder is the sign of Numerator.
4- 2 = 2;
10) What is the output of the C Program.?
int main()
{
int a= 3 + 5/2;
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
A) 3
B) 2
C) 5
D) Can not assign an expression to variable at the time of declaration.
Answer [=] C
Explanation:
Assignment Operator = in C language has the least priority. So the right hand side expression is evaluated first and then assigned to the left side variable.
a = 3 + 5/2;
And a = 3 + 2;
a = 5;